- carapace
- (
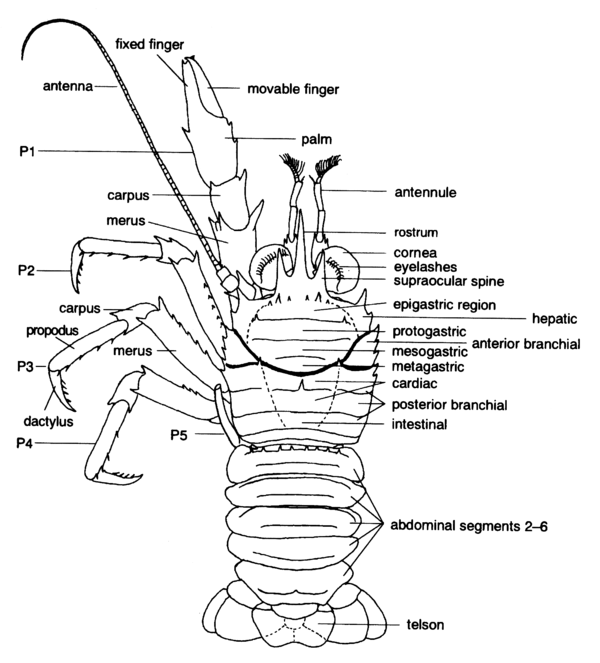 ) [Baba, 2005].Entire animal, right appendages omitted, dorsal view, based on Munida. [Baba, 2005](
) [Baba, 2005].Entire animal, right appendages omitted, dorsal view, based on Munida. [Baba, 2005](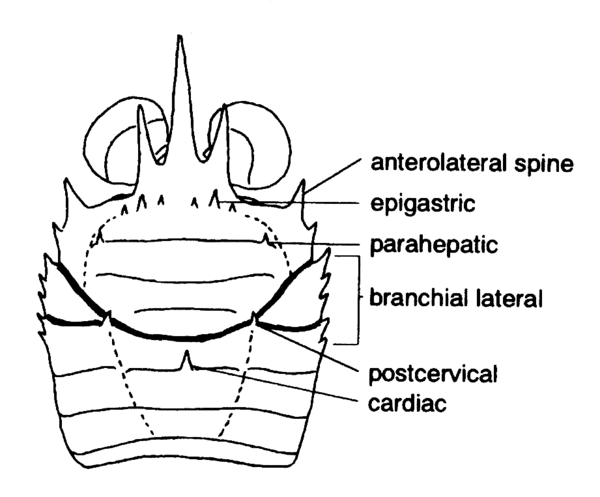 ) [Baba, 2005].Carapace, spines, based on Munida. [Baba, 2005]"Head Shield" cuticular structure arising from posterior margin of cephalon, extending anteriorly and posteriorly, and covering the cephalothoracic somites of the body (Fig. 1) [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997]."Shield" (exoskeleton) overlying cephalothoracic somites of body (see Figs. 13,14) [Hobbs and Jass, 1988]."Head shield" covering the cephalothoracic somites of the body [Butler, T.H.].A more expansive structure than the head shield (cephalic shield) , comprising the head shield and a large fold of the exoskeleton that probably arises (primitively) from the maxillary somite [Brusca and Brusca, 2002].A sheet of cuticle extending back from the head to enclose the dorsal and lateral parts of the thorax; the 'shell' of a crab (Fig. 1) [Warner, 1977].A shield that covers the head and thorax [Mauchline, 1984].an extension of the exoskeleton which covers and fuses with the head and the first two thoracic somites [Holdich and Jones, 1983].Cuticular, usually calcified, structure arising from posterior margin of cephalon, extending anteriorly and posteriorly, often covering head and thorax (cf. Eucarida); also fold of integument extending from maxillary segment, forming bivalved shell of cyprid larvae and of ascothoracicans and mantle of other cirripedia; mantle usually with calcified plates in thoracicans [McLaughlin, 1980].Cuticular, varyingly calcified structure comprising cephalic shield and fold of integument arising from posterior border of maxillary somite extending over trunk, usually covering it laterally as well as dorsally; commonly fused to one or more thoracic somites and in may forms having mid-dorsal hinge [Moore and McCormick, 1969].Shield arising from posterior margin of head and comprising lateral extensions of thoracic somites covering all or most of cephalothorax [Poore, 2004].The "head shield" covering the cephalothoracic somites of the body [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].The "head shield" overlying the cephalothoracic somites of the body [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].The exoskeleton that covers the dorsal and ventro-lateral portions of the cephalothorax [Ingle, 1980].The portion of the hard exoskeleton, or shell, that covers all or part of the body of many crustaceans; in shrimps, lobsters, and crabs, the carapace covers the head and thorax [Bliss, 1982].(Order Cladocera):Single-piece (univalved) shield which, if fully developed, covers only posterior part of body (trunk). Laterally compressed, with ventral gape, and therefore occasionally described as bivalved (i.e., consisting of two "valves" ). (angular, circular, elongate, oval, ovate, ovoid, spherical, subcircular, subquadrate; laterally compressed, thick-bodied; with/without carapace spine, with/without crest, narrowed and prolonged/not narrowed and prolonged posteriorly into short tube, anterior portion swollen/not swollen, with/without projection on anteroventral margin, ventral margin smooth/with fine spines, dorsal margin smooth/serrate; sculpture: reticulated, smooth; longitudinally, obliquely, transversely striated; with/without hairs, with polygonal or rhomboid markings). (Syn. shell) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Notostraca):Large broad shield covering dorsal surface of head, thorax, and anterior part of abdomen. Consists of single element (univalve) and is emarginated (notch, sinus) posteriorly. Bears median eye, compound eyes, and dorsal organ anteriorly and is sculptured by median keel and transverse mandibular and cervical grooves. (Syn. dorsal shield) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Diplostraca):Bivalved, laterally compressed shield typically enclosed entire body; consists of two valves with dorsal hinge line, although occasionally interpreted as representing a single continuous element. Joined to body by ligament and pair of adductor muscles in head region. (broadly oval, compressed, globose = globular, oblong, ovate, subovate, subrectangular, subspherical, swollen, thick and globose, thin and pellucid; with/without growth lines; with/without umbones; with/without keel; sculpture: polygonal, punctate, reticulate, with dendritic or radial grooves, with striae). (Syn. shell) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Cumacea):Large, shield-like structure covering head and three to six thoracic somites. Extends laterally to enclose branchial chamber. Regionated to form anterior pseudorostrum, frontal lobe, ocular lobe, as well as branchial and cardiac regions. (inflated, laterally compressed; dorsal outline: straight, arched, with slight undulations; with/without lateral horns; smooth, sculptured: hairy, rugose, with denticles, with median/lateral carina, with longitudinal depressions, with dorsal crest: serrate, smooth, with teeth) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Tanaidacea):Shield-like structure covering head and first two thoracic segments (thoracomeres). Extends laterally to enclose branchial chamber. See: cephalothorax [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Decapoda):Large, shield-like cuticular structure covering cephalothorax; bears rostrum anteriorly and is typically regionated and sculptured with various carinae, grooves, spines, and teeth. Encloses gill-bearing bases of thoracopods and thus forms branchial chambers. (general form: cylindrical, compressed, depressed; shape: convex, circular, globular, hemispherical, hexagonal, octagonal, orbicular, oval, ovate triangular, pentagonal, polygonal, pyriform, quadrilateral, rectangular, subcircular, subcylindrical, subglobose, subhexagonal, suborbicular, subovoid, subpenta-gonal, subquadrate, subquadrilateral, sub-triangular, transversely oval, tumid; surface: areolated, carinate, eroded, glabrous, granulate, nodular, nodulose, plicate, polished, pubescent, punctuate, with rugae, smooth, squamose, tuberculate, wrinkled) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Mysida):Shield-like structure coving head and most of thorax. Typically fused to first three thoracic segments (thoracomeres) and typically bearing rostrum. (with/without rostrum; undecorated, ornamented: spinose, with keels; posterior margin: indented, produced into spines, with lobes) (see also cervical sulcus) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Stomatopoda):Shield-like cuticular structure covering cephalon (except for anterior acron and antennular somite) as well as first four thoracic somites (thoracomeres); overlaps but does not enclose bases of first five thoracopods. Broad, flattened, and typically sculptured with various carinae and grooves. Bears rostrum anteriorly. (with/without carinae; anterolateral corners: armed, unarmed, rounded) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Leptostraca):Large shield covering thorax, posterior part of head, and anterior part of abdomen. Laterally compressed and therefore often described as being bivalved (although no dorsal hinge is present). Two halves of carapace can be drawn toward each other by carapace adductor muscle. Bears rostral plate anteriorly. (elliptical and posterodorsally truncate, subtriangular and posteriorly acuminate; smooth, with polygonal ornamentation) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Branchiura):Dorsoventrally flattened, shield-like structure covering head and first thoracic somite (thoracomere); characterized by pair of posterolateral wing-like extensions (alae). Bears pair of compound eyes dorsolaterally and set of median nauplius eyes. (circular, cordate, elliptical, trifoliate) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Cirripedia):Mantle [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Ostracoda):Lateral outfolds of dorsal epithelium and cuticle, bivalved and enveloping the entire body [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].(Class Ostracoda):Shell-like outer covering; consists of pair of valves joined dorsally by hinge and entirely enclosing body. (calcareous, uncalcified; ornate, smooth; amplete, postplete, preplete) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Thermosbaenacea):Shield-like structure fused to and covering head and first thoracic somite (thoracomere). Extends posteriorly and laterally to cover additional thoracomeres. Serves in respiration and forms brood pouch in female [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Euphausiacea):Shield-like, relatively thin structure fused to thoracic somites and covering cephalothorax. Does not enclose gill-bearing bases of thoracopods. Typically bears cervical groove; (with/without rostrum) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
) [Baba, 2005].Carapace, spines, based on Munida. [Baba, 2005]"Head Shield" cuticular structure arising from posterior margin of cephalon, extending anteriorly and posteriorly, and covering the cephalothoracic somites of the body (Fig. 1) [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997]."Shield" (exoskeleton) overlying cephalothoracic somites of body (see Figs. 13,14) [Hobbs and Jass, 1988]."Head shield" covering the cephalothoracic somites of the body [Butler, T.H.].A more expansive structure than the head shield (cephalic shield) , comprising the head shield and a large fold of the exoskeleton that probably arises (primitively) from the maxillary somite [Brusca and Brusca, 2002].A sheet of cuticle extending back from the head to enclose the dorsal and lateral parts of the thorax; the 'shell' of a crab (Fig. 1) [Warner, 1977].A shield that covers the head and thorax [Mauchline, 1984].an extension of the exoskeleton which covers and fuses with the head and the first two thoracic somites [Holdich and Jones, 1983].Cuticular, usually calcified, structure arising from posterior margin of cephalon, extending anteriorly and posteriorly, often covering head and thorax (cf. Eucarida); also fold of integument extending from maxillary segment, forming bivalved shell of cyprid larvae and of ascothoracicans and mantle of other cirripedia; mantle usually with calcified plates in thoracicans [McLaughlin, 1980].Cuticular, varyingly calcified structure comprising cephalic shield and fold of integument arising from posterior border of maxillary somite extending over trunk, usually covering it laterally as well as dorsally; commonly fused to one or more thoracic somites and in may forms having mid-dorsal hinge [Moore and McCormick, 1969].Shield arising from posterior margin of head and comprising lateral extensions of thoracic somites covering all or most of cephalothorax [Poore, 2004].The "head shield" covering the cephalothoracic somites of the body [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].The "head shield" overlying the cephalothoracic somites of the body [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].The exoskeleton that covers the dorsal and ventro-lateral portions of the cephalothorax [Ingle, 1980].The portion of the hard exoskeleton, or shell, that covers all or part of the body of many crustaceans; in shrimps, lobsters, and crabs, the carapace covers the head and thorax [Bliss, 1982].(Order Cladocera):Single-piece (univalved) shield which, if fully developed, covers only posterior part of body (trunk). Laterally compressed, with ventral gape, and therefore occasionally described as bivalved (i.e., consisting of two "valves" ). (angular, circular, elongate, oval, ovate, ovoid, spherical, subcircular, subquadrate; laterally compressed, thick-bodied; with/without carapace spine, with/without crest, narrowed and prolonged/not narrowed and prolonged posteriorly into short tube, anterior portion swollen/not swollen, with/without projection on anteroventral margin, ventral margin smooth/with fine spines, dorsal margin smooth/serrate; sculpture: reticulated, smooth; longitudinally, obliquely, transversely striated; with/without hairs, with polygonal or rhomboid markings). (Syn. shell) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Notostraca):Large broad shield covering dorsal surface of head, thorax, and anterior part of abdomen. Consists of single element (univalve) and is emarginated (notch, sinus) posteriorly. Bears median eye, compound eyes, and dorsal organ anteriorly and is sculptured by median keel and transverse mandibular and cervical grooves. (Syn. dorsal shield) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Diplostraca):Bivalved, laterally compressed shield typically enclosed entire body; consists of two valves with dorsal hinge line, although occasionally interpreted as representing a single continuous element. Joined to body by ligament and pair of adductor muscles in head region. (broadly oval, compressed, globose = globular, oblong, ovate, subovate, subrectangular, subspherical, swollen, thick and globose, thin and pellucid; with/without growth lines; with/without umbones; with/without keel; sculpture: polygonal, punctate, reticulate, with dendritic or radial grooves, with striae). (Syn. shell) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Cumacea):Large, shield-like structure covering head and three to six thoracic somites. Extends laterally to enclose branchial chamber. Regionated to form anterior pseudorostrum, frontal lobe, ocular lobe, as well as branchial and cardiac regions. (inflated, laterally compressed; dorsal outline: straight, arched, with slight undulations; with/without lateral horns; smooth, sculptured: hairy, rugose, with denticles, with median/lateral carina, with longitudinal depressions, with dorsal crest: serrate, smooth, with teeth) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Tanaidacea):Shield-like structure covering head and first two thoracic segments (thoracomeres). Extends laterally to enclose branchial chamber. See: cephalothorax [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Decapoda):Large, shield-like cuticular structure covering cephalothorax; bears rostrum anteriorly and is typically regionated and sculptured with various carinae, grooves, spines, and teeth. Encloses gill-bearing bases of thoracopods and thus forms branchial chambers. (general form: cylindrical, compressed, depressed; shape: convex, circular, globular, hemispherical, hexagonal, octagonal, orbicular, oval, ovate triangular, pentagonal, polygonal, pyriform, quadrilateral, rectangular, subcircular, subcylindrical, subglobose, subhexagonal, suborbicular, subovoid, subpenta-gonal, subquadrate, subquadrilateral, sub-triangular, transversely oval, tumid; surface: areolated, carinate, eroded, glabrous, granulate, nodular, nodulose, plicate, polished, pubescent, punctuate, with rugae, smooth, squamose, tuberculate, wrinkled) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Mysida):Shield-like structure coving head and most of thorax. Typically fused to first three thoracic segments (thoracomeres) and typically bearing rostrum. (with/without rostrum; undecorated, ornamented: spinose, with keels; posterior margin: indented, produced into spines, with lobes) (see also cervical sulcus) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Stomatopoda):Shield-like cuticular structure covering cephalon (except for anterior acron and antennular somite) as well as first four thoracic somites (thoracomeres); overlaps but does not enclose bases of first five thoracopods. Broad, flattened, and typically sculptured with various carinae and grooves. Bears rostrum anteriorly. (with/without carinae; anterolateral corners: armed, unarmed, rounded) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Leptostraca):Large shield covering thorax, posterior part of head, and anterior part of abdomen. Laterally compressed and therefore often described as being bivalved (although no dorsal hinge is present). Two halves of carapace can be drawn toward each other by carapace adductor muscle. Bears rostral plate anteriorly. (elliptical and posterodorsally truncate, subtriangular and posteriorly acuminate; smooth, with polygonal ornamentation) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Branchiura):Dorsoventrally flattened, shield-like structure covering head and first thoracic somite (thoracomere); characterized by pair of posterolateral wing-like extensions (alae). Bears pair of compound eyes dorsolaterally and set of median nauplius eyes. (circular, cordate, elliptical, trifoliate) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Cirripedia):Mantle [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Ostracoda):Lateral outfolds of dorsal epithelium and cuticle, bivalved and enveloping the entire body [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].(Class Ostracoda):Shell-like outer covering; consists of pair of valves joined dorsally by hinge and entirely enclosing body. (calcareous, uncalcified; ornate, smooth; amplete, postplete, preplete) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Thermosbaenacea):Shield-like structure fused to and covering head and first thoracic somite (thoracomere). Extends posteriorly and laterally to cover additional thoracomeres. Serves in respiration and forms brood pouch in female [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Euphausiacea):Shield-like, relatively thin structure fused to thoracic somites and covering cephalothorax. Does not enclose gill-bearing bases of thoracopods. Typically bears cervical groove; (with/without rostrum) [Stachowitsch, 1992].
Crustacea glossary. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. 2011.
